VISION PERFORMANCE: KEEPING OUR EYES ON THE BALL

SPORTS THROUGH A DIFFERENT LENS
The elite operate with visual performance-shaping skills most people never develop.
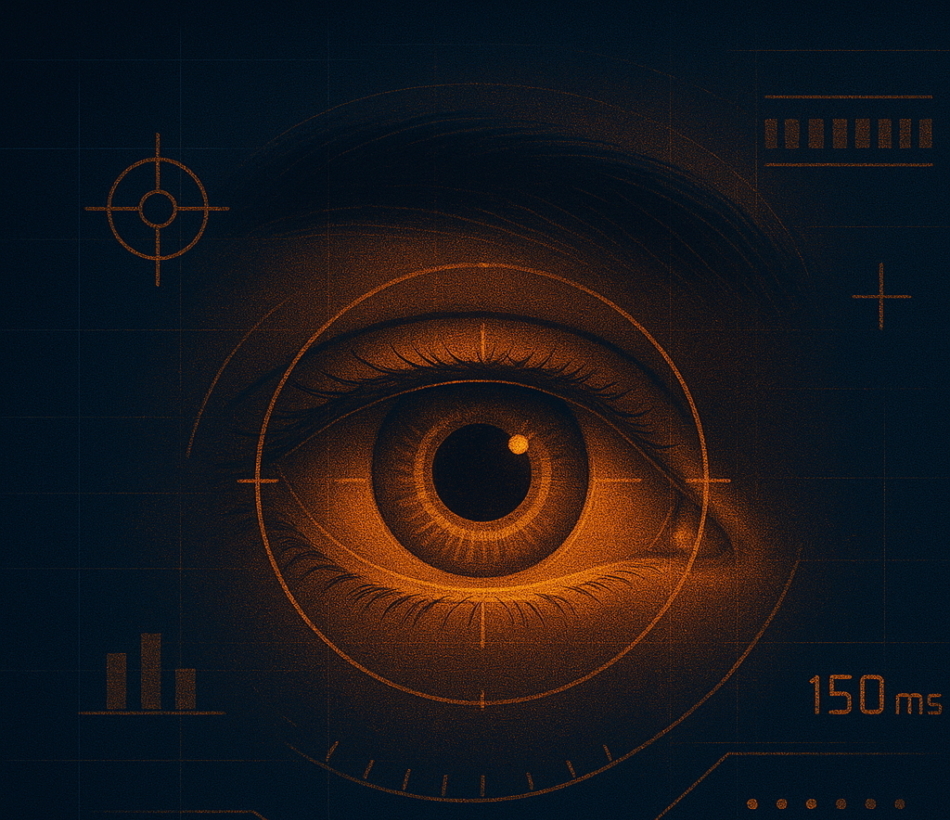
Consider a baseball hitter who has less than 150 milliseconds to spot a 100-mph pitch and decide whether to swing. A F1 driver who needs to set his gaze, mid-turn, on the next corner's entry. Sharpshooter who breaches beyond the theoretical perfect 20/20 vision or employs the quiet eye–fixating on the ball or target to buy his brain crucial processing time.
Such display of dynamic visual acuity, reaction speed, depth perception and visual focus shapes every micro-adjustments, and determines whether an athlete anticipates or reacts, stays upright or tumbles.
Yet, visual skills rarely appear in scouting reports or athlete development programs. Under-recognized, under-measured, and under-trained–eyesight and acuity are performance enablers hiding in plain sight.
HOW ATHLETES HACK THE SYSTEM
Elite performers literally see the game differently.
But deliberately training how visual information is captured, processed, and converted into action allows simple drills to compound into meaningful gains across the visual–motor loop.
1. Stabilizing the Visual Field
Achieved by strengthening retinal and ocular muscles through oculomotor work such as moving object tracking or saccade ladders. Athletes also hold a fixed gaze under fatigue or simulated game chaos to train stability amid the neural noise of high-pressure environments.
2. Compressing the Decision Loop
Gamified late visual cue drills and rapid discrimination tasks using light flashes, color calls, decision targets can shorten reaction speeds.
3. Expanding Spatial Bandwidth
In sports where speed, trajectory and distance judging decide outcomes, athletes can sharpen depth perception & contrast sensitivity by alternating between near–far targets or training under variable lighting. Peripheral awareness can be expanded by reading motion at the edges of the visual field, reinforcing spatial orientation in fast-moving environments.
In unilateral sports, training the dominant eye is standard–but loading the weaker eye with targeted drills can unlock marginal gains in spatial precision.
Beyond the eye chart - Light boards, eye-tracking wearables, smart screens, and VR systems are moving into training rooms to map, train and optimize visual system dynamics. The addition of this new data layer in the sports performance stack closes a critical blind spot and is creating a sports tech opportunity.
REPURPOSING VISION IN THE MODERN LIFE
Vision may feel effortless, but the simple act of seeing depends on complex dynamic optical tissues converting, multiple times per second, photons into electrical signals for the brain to reconstruct three-dimensional dynamic worlds.
An evolutionary gaze - Long before athletic performances were a matter for competition, visual acuity was a survival tool–hardwired for threat and movement detection, alternating between two modes :
- Panoramic vision: A wide scanning gaze, relaxed retina, reduced sympathetic load, and stabilized mood.
- Tunnel vision: A narrow, retina-contracted and heightened alertness fight-or-flight state associated with epinephrine release.
Modern life—safe, screen-driven, and largely spent indoors—now traps most of us in that second mode. The result: near-focus dominates, the retina remains under constant strain, and the sympathetic nervous system overloads.
This is precisely where the visual skills and drills honed by athletes become relevant beyond the playing field–offering practical levers to regulate stress and restore focus & well-being.
1. Before cognitively demanding work, hold your gaze on a precise, empty point in near space for 60–90 seconds to shift the brain into information-gathering mode.
2. Between prolonged deep work blocks, lift the gaze, raise the chin, and open the eyes wide to restore panoramic vision–a visual and nervous system rest & reset and natural wake-up.
3. After screen-heavy days, controlled red-light exposure may offset photoreceptor and mitochondrial metabolic strain from prolonged near-sighted focus.
Visual drills are making their way into everyone’s pocket with gamified app like brainpro, eye hero, opticstrainer and the likes.
LONG-TERM VISION
Longevity - Decades of visual overload make visual impairment the default trajectory.
Near-focus dominance accelerates presbyopia. Protein and cellular debris cloud the lens and contribute to cataracts. Intraocular pressure buildup increases glaucoma risk. Lifestyle stressors layer on genetic predispositions to accelerate macular degeneration.
But the downward trajectory is avoidable.
Lifestyle - Aerobic exercise, movement generating continuous optical flow (e.g. trail running), proprioceptive drills and time spent outdoors all keep the visual & vestibular systems actively engaged and resilient.
Diagnostic and rehab - The eye can also serve as a window into cardiometabolic health. Retinal microvascular imaging reveal early signs of atherosclerosis and Type 2 Diabetes-linked vascular dysfunctions. Plus, tight oculomotor coupling makes visual assessment and training cornerstone of concussion diagnostics & recovery and PTSD management.
In a world where everything in and around training is optimized, the untapped edge is how the game is seen–and how long the brain stays sharp.